Cost of Disinflation: Sacrifice Ratio With Diagram
Understanding the sacrifice ratio and implementing appropriate policies can help strike the right balance between inflation control and economic growth, ensuring sustainable and prosperous economies. The sacrifice ratio in economics was first developed in the 1950s in association with the Phillips curve, a curve that depicted a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment. Originally this relationship was thought to be permanent, but that was proven wrong during the 1970s and the events thereafter, and has since been modified to fit a short-term perspective.
Alternative Approaches to Balancing Inflation and Unemployment
An analysis of the ratio would show how the country could answer assuming the level of inflation changes by 1%. A higher level of inflation is many times brought about by strong economic growth. For instance, in the event that aggregate demand extends quicker than aggregate supply in an economy, the outcome is higher inflation. In the event that an economy is facing inflation, central banks have tools they can use to slow economic growth in a bid to reduce inflationary tensions. Policymakers can use the sacrifice ratio as a tool to evaluate the potential costs of anti-inflation measures.
The Costs and Benefits of Reducing Inflation
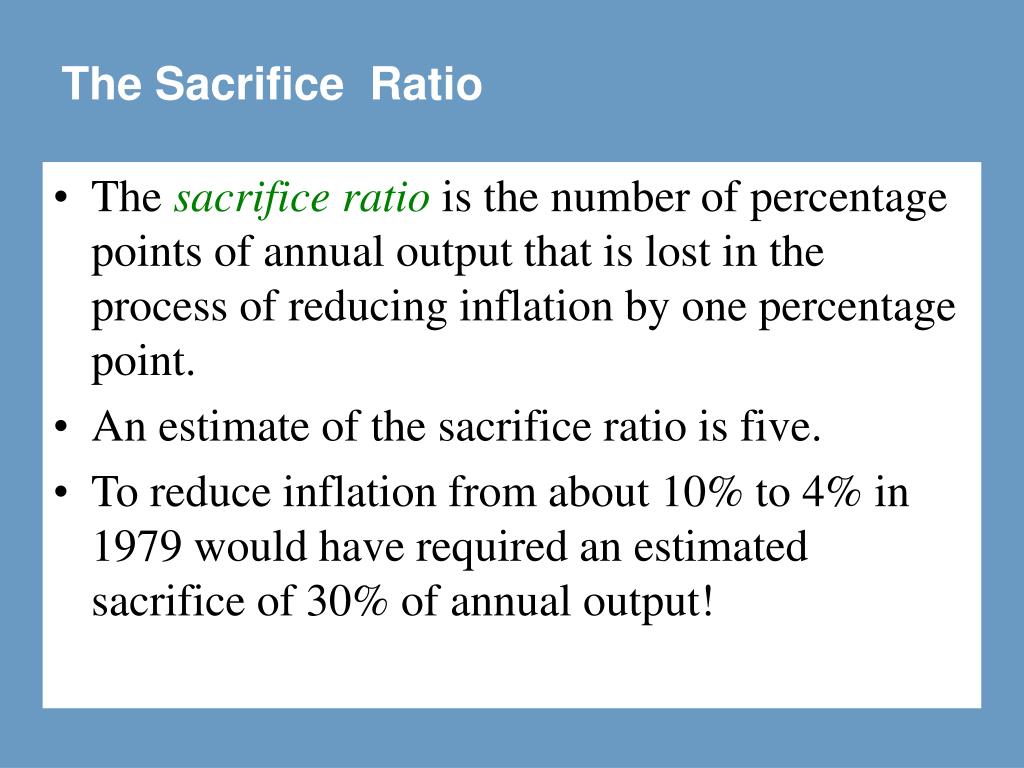
Inflation rate is decreased from 10 to 4% over 3 years at the cost of output 10%, 8% and 6% below the potential output (full employment) in first, second and third year, respectively. It means for every 1% reduction in inflation, an economy must sacrifice the 5% of annual output. That being said, let’s now take a detailed look at the sacrificing ratio and the exact situations under which it is most effective. Combining the Phillips curve tradeoff of the 1960s with Okun's law would, via the formula above, give a sacrifice ratio of about 2.0 for the 1960s, which is reasonably consistent with Ball's research.
Related terms
- However, the potential reduction in output in response to falling prices may help the economy in the short term to reduce inflation also, and the sacrifice ratio measures that cost.
- Using the short-run Phillips curve with inflation expectations held constant, we can estimate how much the unemployment rate will rise when the inflation rate falls by one percentage point.
- It seems that the economy may be facing a catastrophic recession of a magnitude not seen since the Great Depression of the 1930s may be on the horizon.
- Finally, point C exhibits a time when inflation reduces without causing unemployment.
- Brand loyalty programs are a cornerstone of customer retention strategies for businesses across…
In response, many of these countries implemented austerity measures to restore fiscal discipline and regain the trust of financial markets. When it comes to macroeconomics, one of the most discussed topics is the relationship between inflation and unemployment. This connection, often referred to as the Phillips curve, suggests that there is a trade-off between these two economic variables. In simpler terms, when inflation is low, unemployment tends to be high, and vice versa.

Understanding these factors is vital for policymakers and economists alike as they strive to strike a balance between these two variables. Reducing inflation is a policy objective that comes with both costs and benefits. It is important for policymakers to carefully consider these trade-offs and strike a balance that promotes sustainable economic growth. Looking back at history, we can find examples where countries have faced high sacrifice ratios during periods of inflation reduction. One such case is the United States in the early 1980s when the Federal Reserve implemented tight monetary policy to combat high inflation. The sacrifice ratio during this period was estimated to be around 5, indicating that a 5% reduction in output was required for every 1% decrease in inflation.
How to Beat Stagflation (with a case study)
The sacrifice ratio is typically calculated by economists using empirical data and statistical models. It is calculated as the percentage reduction in output that is needed to achieve a 1% reduction in inflation. For instance, if the sacrifice ratio is 2, it means that a 2% reduction in output is required for every 1% reduction in inflation. The inflation rate in an economy has diminished from 10 to 5% more than three years at the cost of output 11%, 9%, and 5% for every year, giving a total loss of 25%. Sacrifice ratios will also appear to be volatile in these circumstances because the output will not be as volatile. In fact, even in more stable times it may be better to use core inflation as the variable for calculating sacrifice ratios because it is inherently less volatile.
The ratio primarily measures the short-term costs of reducing inflation, often overlooking the long-term benefits that may arise from lower inflation rates. Critics argue that placing too much emphasis on minimizing the sacrifice ratio may lead to neglecting important long-term considerations, such as sustainable economic growth and stability. The sacrifice ratio is a concept that holds great importance in the field of economics and monetary policy. It refers to the trade-off between the short-term costs and the long-term benefits of reducing inflation. In simple terms, it quantifies the economic output that must be sacrificed, or the costs that must be endured, in order to achieve a desired reduction in inflation. The sacrifice ratio is a concept that further explores the relationship between inflation and unemployment.
In this manner, to stay away from a recession, the government needs to track down the least costly method for diminishing inflation. In 2022, with inflation rates soaring to levels not seen since the 1970s, sacrifice ratio formula most western countries are facing some very difficult choices in the years ahead. Reducing inflation is going to be necessary if a complete collapse of the fiat monetary system is to be avoided.
